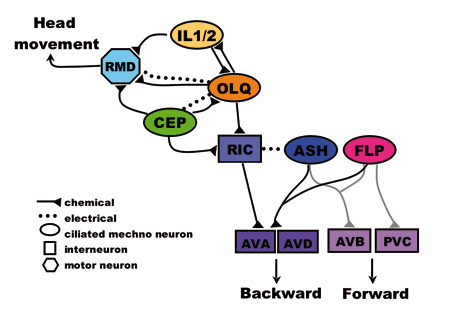
Mechanosensation and nociception Nematodes sense touch stimuli using molecules that are conserved with humans
and other mammals. We are interested in the molecular basis of mechanotransduction
in neurons, and have characterized the how members of the TRP and DEG/ENaC channel families affect the functions of specific nematode touch neurons. These
molecules also function in polymodal nociceptors, which sense painful
touch as well as as noxious chemicals. We are also interested in
how touch sensory information is integrated in
the worm
brain,
and
how
worms
remember
touch sensory
information.
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
 |
|
Here is a movie of a worm responding to body touch. The worm switches from crawling
forward to crawling backward, a simple escape reflex.
This worm is immobilized with glue, and is being stimulated by a mechanical probe on its
nose. The stimulus shown activates nose touch neurons called OLQ.
Here is a psuedocolour movie of a body touch neuron responding to touch. Red indicates
calcium influx accompanying neuronal excitation. |
| |
|
|
|
|
Recent papers:
Sensory transduction in nociceptors and touch neurons:
Kindt KS, Viswanath V, Macpherson L, Quast K, Hu H, Patapoutian A, Schafer WR
(2007) “Caenorhabditis elegans TRPA-1 functions in mechanosensation.” Nature Neurosci 10: 568-577. Epub 2007 Apr 22. Supplemental material.
Frøkjær-Jensen C, Kindt KS, Kerr RA, Suzuki H, Melnik-Martinez K, Gerstbrein B, Driscoll
M, Schafer WR (2006) "Effects of voltage-gated calcium channel subunit genes on calcium influx in cultured
C. elegans mechanosensory neurons" J. Neurobiol. 66: 1125-1139 Epub 2006 Jul 11 Hilliard MA, Apicella AJ, Kerr R, Suzuki H, Bazzicalupo P, Schafer WR. (2005) "In vivo imaging of C. elegans ASH neurons: cellular response and adaptation to
chemical repellents" EMBO Journal 24: 63-72. Epub 2004 Dec 02.
Kahn-Kirby AH, Dantzker JLM, Apicella AJ, Schafer WR, Browse J, Bargmann CI,
Watts JL (2004) "Specific polyunsaturated fatty acids drive TRPV-dependent sensory signaling in
vivo" Cell 19: 889-900.
Fukuto HS, Ferkey DM, Apicella AJ, Lans H, Sharmeen T, Chen W, Lefkowitz RJ,
Jansen G, Schafer WR, Hart AC. (2004) "G Protein-coupled receptor kinase function is essential for chemosensation in
C. elegans" Neuron 42: 581-593. Suzuki H, Kerr R, Bianchi L, Frøkjær-Jensen C, Slone D, Xue J, Gerstbrein B, Driscoll M, Schafer WR. (2003) "In vivo functional analysis of C. elegans mechanosensory neurons reveals a specific
role for MEC-4 channels in the process of gentle touch transduction" Neuron 39: 1005-1017.
|
|
|
Sensory circuits:
Kindt KS, Quast KB, Giles AG, De S, Hendrey D, Nicastro I, Rankin CH, Schafer
WR (2007) "Dopamine mediates context-dependent modulation of sensory plasticity in C. elegans" Neuron 55: 662-676. Supplemental material.
Tomioka M, Adachi T, Suzuki H, Kunitomo H, Schafer WR, Iino Y (2006) "The insulin/PI3 –kinase pathway regulates salt chemotaxis learning in Caenorhabditis elegans" Neuron 51: 613-626 Sanyal S, Wintle RF, Kindt K, Nuttley WM, Arvan R, Fitzmaurice P, Bigras E, Merz
D, Hebert TE, van der Kooy D, Schafer WR, Culotti JG and
Van Tol HHM. (2004) "Dopamine modulates the plasticity of mechanosensory responses in C. elegans" EMBO Journal 23: 473-482.
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
