2025
Röper, K*. (2025) Supracellular actomyosin assemblies: master coordinators of development. Development 15; 152 (16): dev204896. doi: https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.204896
May, A. and Röper, K*. (2025) Single-cell analysis of the early Drosophila salivary gland reveals that morphogenetic control involves both the induction and exclusion of gene expression programs. PLOS Biology 23, e3003133. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3003133
2024
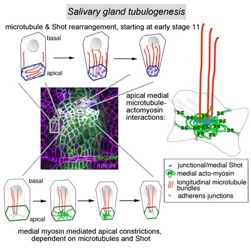
Gillard, G. and Röper, K* (2024). b–H-Spectrin is a key component of an apical-medial hub of proteins during cell wedging in tube morphogenesis. J. Cell Science 137 (15): jcs261946. (featured as cover picture and ‘Research Highlights’)

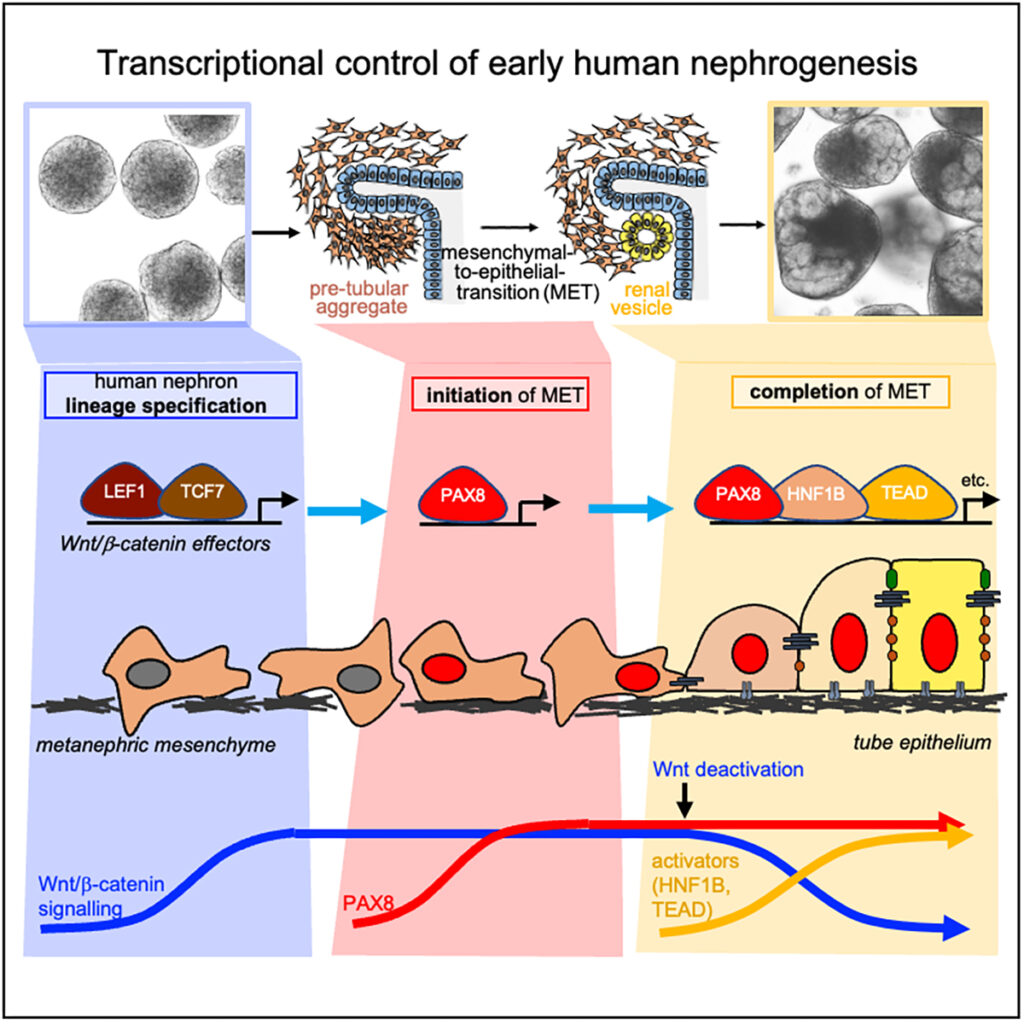
Ng-Blichfeldt, J.-P., Stewart, B.J., Clatworthy, M.R., Williams, J.M., and Röper, K*. (2024) Identification of a core transcriptional program driving the human renal mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition. Developmental Cell (59), 1–18, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2024.01.011, (featured as cover picture)

2023
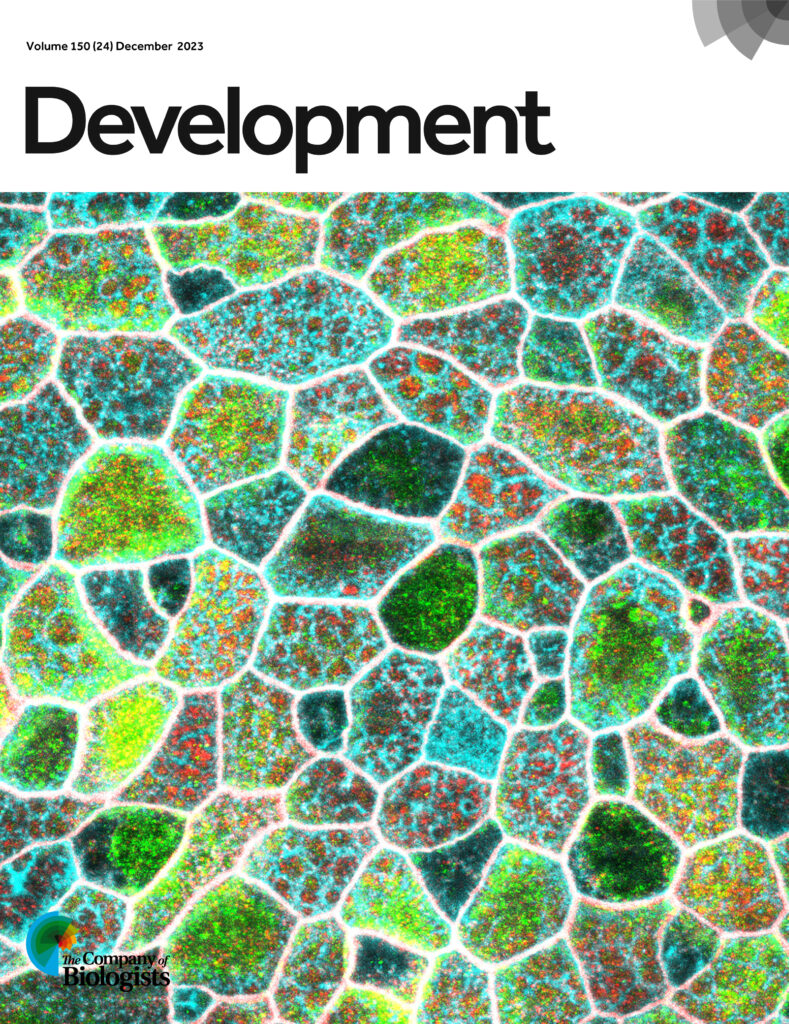
Peterson, J., Balogh Sivars, K. Bianco, A., and Röper, K*. (2023.) Toll-like receptor signalling via IRAK4 affects epithelial integrity and tightness through regulation of junctional tension. Development 150 (24): dev201893; cover picture in Development
Ashour, D.J., Durney, C.H., Planelles-Herrero, V.J., Stevens, T.J., Feng,J.J. and Röper, K*. (2023) Zasp52 strengthens whole embryo tissue integrity through supracellular actomyosin networks. Development 150, dev20123 ; highlighted as Preprint Highlight in MBoC https://www.molbiolcell.org/doi/10.1091/mbc.P22-10-1006; highlighted as Research Highlight in Development; cover picture in Development
2021
Sánchez-Corrales, Y. E., Blanchard, G. B., & Röper, K*. (2021) Correct regionalisation of a tissue primordium is essential for coordinated morphogenesis. eLife; 2021;0:e72369. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.72369
Gillard, G., Girdler, G. & Röper, K. (2021). A release-and-capture mechanism generates an essential non-centrosomal microtubule array during tube budding. Nature Communications 12: 4096 https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-24332-0
2020
Ambrosini, A., and Röper K. (2020) “Neur”al brain wave: Coordinating epithelial-to-neural stem cell transition in the fly optic lobe. Invited Spotlight for J. Cell Biol. 219(11):e202009040. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202009040.
Ng-Blichfeldt, J.-P. and Röper, K. (2020). Mesenchymal to epithelial transitions (MET) in development and cancer and the role of MET-TFs. Invited review for Methods in Molecular Biology 2179, ISBN 978-1-0716-0778-7
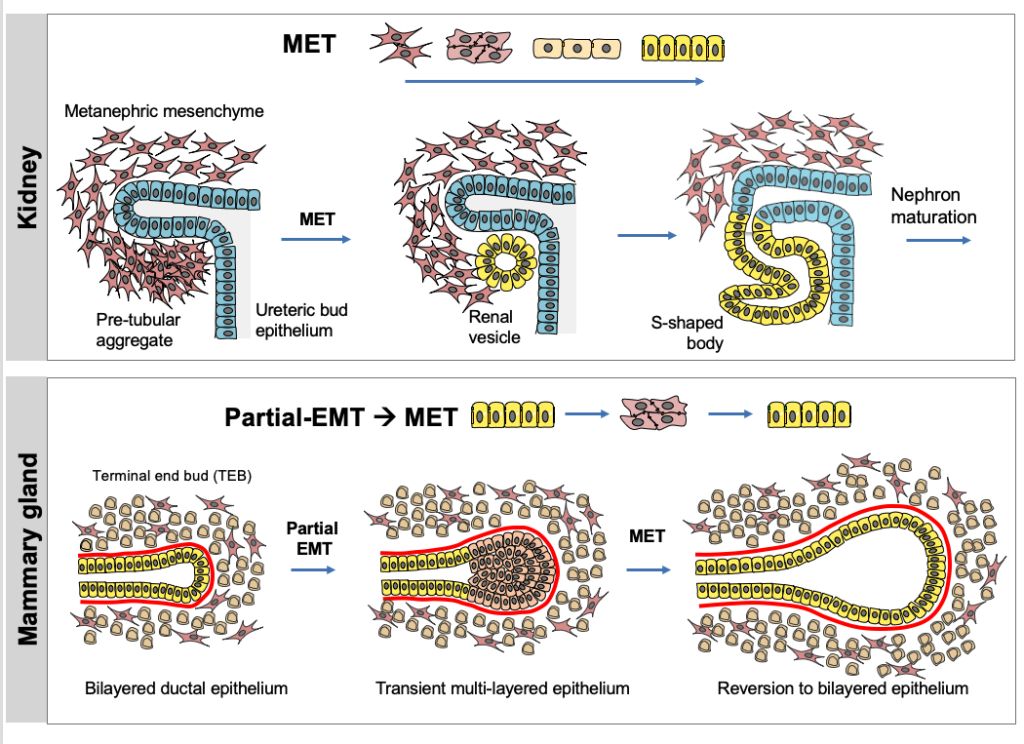
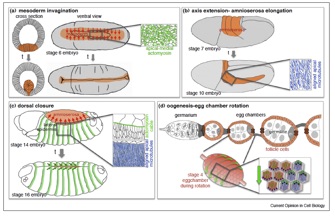
Gillard, G.,and Röper, K. (2020). Control of cell shape during epithelial morphogenesis: recent advances.Invited review for Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 63: 1-8, doi.org/10.1016/j.gde.2020.01.003
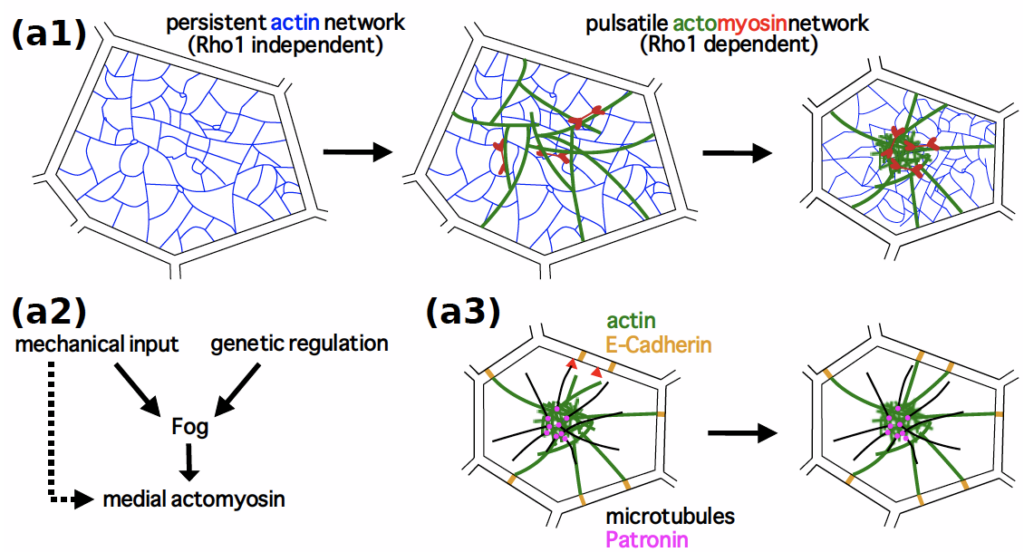
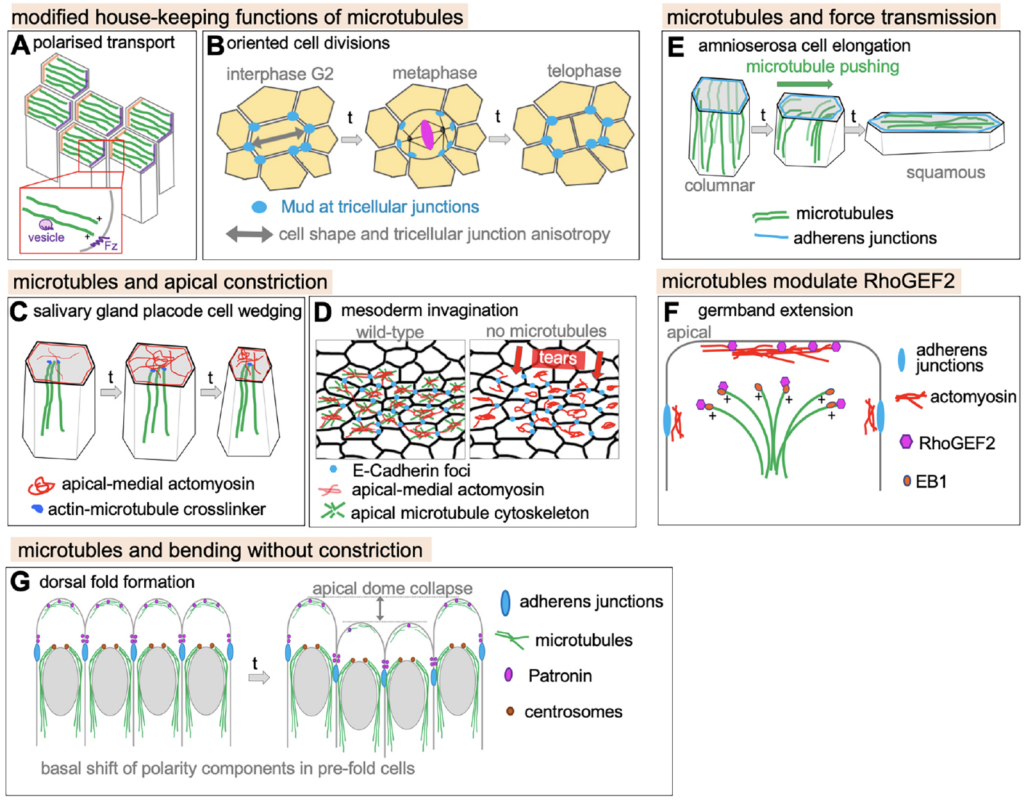
Röper, K. (2020) Microtubules enter centre stage for morphogenesis. Invited review for Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B, Biol. Sci.375, 20190557, DOI : 10.1098/rstb.2019.0557
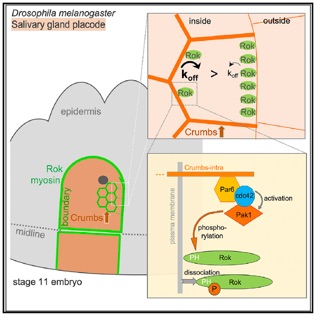
Sidor, C., Stevens, T., Jin, L., Boulanger, J., Röper, K. (2020). Rho kinase planar polarisation at tissue boundaries depends on phospho-regulation of membrane residence time, Developmental Cell, 52: 364–378., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2019.12.003
2018
Röper, K. (2018) Quantitative imaging and the effect of tissue topology on morphogenesis. Developmental Cell. 47(5):537-538. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2018.11.023.; PMID: 30513296
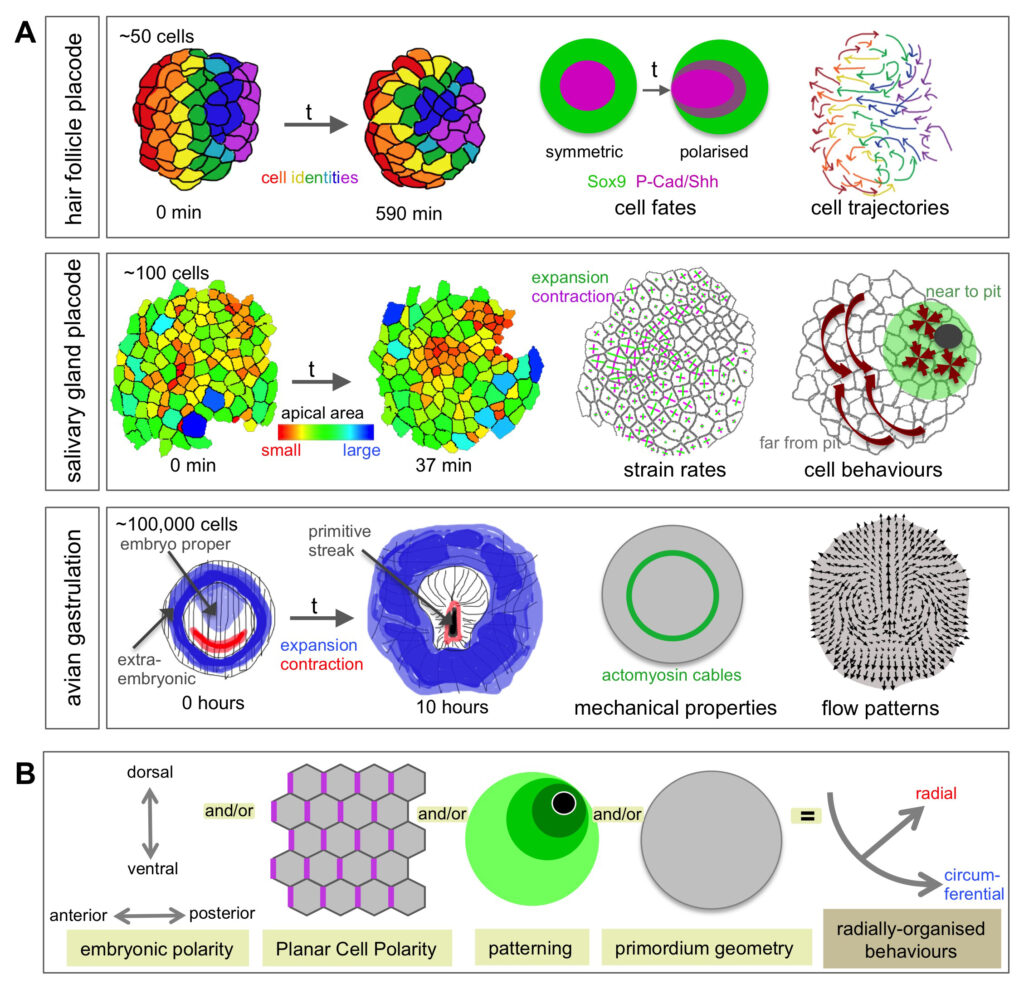
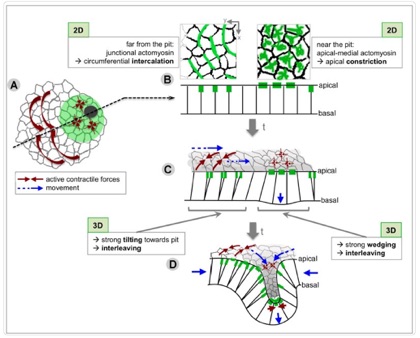
Sánchez-Corrales, Y.E., Röper K. (2018). Radially-patterned cell behaviours during tube budding from an epithelium. eLife;7:e35717 DOI: 10.7554/eLife.35717
Röper, K., and Bustelo, X.R. (2018) Editorial overview: New concepts and experimental approaches to understand development, tissue regeneration, and human disease. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol.; 55:iii-v.; doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2018.09.006.; PMID: 30287131
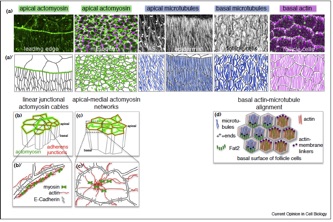
Sánchez-Corrales, Y.E., Röper K. (2018). Alignment of cytoskeletal structures across cell boundaries generates tissue cohesion during organ formation. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 55:104–110 . doi.org/10.1016/j.ceb.2018.07.001
2017
Sidor C, Röper K. (2017). Squeezing out in a “tug of war”: The role of myosin in neural stem cell delamination. J. Cell Biology. 1;216(5):1215-1218. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201702116
Takács, Z., Jankovics, F., Vilmos, P., Lénárt, P., Röper, K., and Erdélyi, M. (2017) The spectraplakin short stop is an essential microtubule regulator involved in epithelial closure in Drosophila., J. Cell Science. 130:712-724.
2016
O’Donnell, M. A. (2016). Katja Röper: Deciphering tissue origami. J. Cell Biology, 215(2), 140–141. http://doi.org/10.1038/nrm3568


Sidor, C. and Röper, K. (2016), Genetic control of salivary gland tubulogenesis in Drosophila. in ‘Organogenetic Gene Networks’ pp 125-149,DOI 10.1007/978-3-319-42767-6_5, ISBN 978-3-319-42765-2 (invited review).
Girdler, G.C., Applewhite, D.A., Perry, W.M.G., Rogers, S.L., and Röper, K. (2016). The Gas2 family protein Pigs is a microtubule +TIP that affects cytoskeleton organisation. J. Cell Science. 129: 121-134.
2015
Röper, K. (2015), Integration of cell-cell adhesion and contractile actomyosin activity during morphogenesis. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 112:103-27.
2014
Girdler, G., and Röper, K. (2014), Controlling cell shape changes during salivary gland tube formation in Drosophila. Sem.Cell Dev.Biol., 1–8. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2014.03.020.
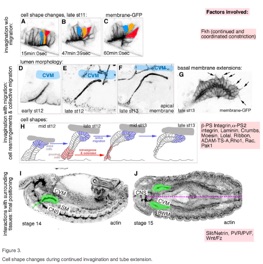
Booth, A.J.R., Blanchard, G.B., Adams, R.J. and Röper, K. (2014), A dynamic microtubule cytoskeleton directs medial actomyosin function during tube formation. Developmental Cell, 29(5), 562–576. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2014.03.023.
2013
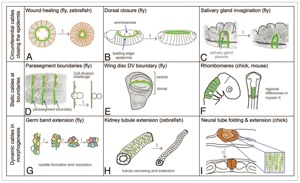
Röper, K. (2013). Supracellular actomyosin assemblies during development. Bioarchitecture, 3(2), 45–49. doi:10.4161/bioa.25339.
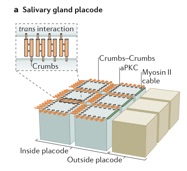
Thompson, B, Pichaud, F. and Röper, K., (2013) Sticking together the Crumbs – an unexpected function for an old friend. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology.14(5), 307–314 (Review)
2012
Röper, K. (2012) Anisotropy of Crumbs and aPKC drives myosin cable assembly during tube formation. Developmental Cell 23:939-953.
2010
Pines, M.K., Housden, B.E., Bernard, F., Bray, S.J., and Röper, K., (2010)The cytolinker Pigs is a direct target and a negative regulator of Notch signalling. Development 137: 913-22. (featured in ‘In this issue’; Faculty of 1000: ‘Recommended’).

2009
Maybeck, V. and Röper, K., (2009) A targeted gain-of-function screen identifies genes affecting salivary gland morphogenesis/tubulogenesis in Drosophila. Genetics 181: 543–565.
2007
Röper, K., (2007) Rtnl1 is enriched in a specialized germline ER that associates with ribonucleoprotein granule components. J. Cell Science. 120: 1081-1092.
2005
Röper, K., Mao, Y., and Brown N.H. (2005) Contribution of sequence variation in Drosophila actins to their incorporation into actin-based structures in vivo. J. Cell Science. 118: 3937-3948. (featured as cover picture).

2004
Röper, K*., and Brown, N.H. (2004) A spectraplakin is enriched on the fusome and organizes microtubules during oocyte specification in Drosophila. Current Biology. 14: 99-110. (*corresponding author).
2003
Röper, K. and Brown, N.H. (2003) Maintaining epithelial integrity: a function for gigantic spectraplakin isoforms in adherens junctions. J. Cell Biology. 162: 1305-1315. (featured in ‘In this issue’ and as cover picture).


2002
Röper K., Gregory S.L., and Brown N.H. (2002) The ‘spectraplakins’: cytoskeletal giants with characteristics of both spectrin and plakin families. J. Cell Science. 115:4215-4225. (Review; Faculty of 1000: ‘Must read’).
Pre Postdoc
Kosodo,Y.*, Röper, K.*, Haubensak, W.*, Marzesco, A.M., Corbeil, D., and Huttner, W.B. (2004) Asymmetric distribution of the apical plasma membrane during neurogenic divisions of mammalian neuroepithelial cells. EMBO J. 23:2314-2324. (* joint first authors; Faculty of 1000: ‘Must read’).
Corbeil D., Röper K., Fargeas C.A., Joester A., and Huttner W.B. (2000) Prominin: a story of cholesterol, plasma membrane protrusions and human pathology. Traffic 2:82-91. (Review).
Röper, K., Corbeil, D., and Huttner, W.B. (2000) Retention of prominin in microvilli reveals distinct cholesterol–based lipid microdomains in the apical plasma membrane. Nature Cell Biol. 2:582-592.
Röper, K., Corbeil, D., and Huttner, W.B. (2000) Microvilli, lipid microdomains and cell polarity: a potential role of the lipid bilayer in the retention of prominin in apical microvillar membranes. NATO Science Series. Protein, lipid and membrane traffic: pathways and targeting. (Edit.: Jos A.F. Op den Kamp), IOS Press, pp73-84. (Book Chapter),
Corbeil, D.*, Röper, K.*, Hellwig, A., Tavian, M., Miraglia, S., Watt, S., Simmons, P., Peault, B., Buck, D.W., and Huttner, W.B. (2000) The human AC133 hematopoietic stem cell antigen is also expressed in epithelial cells and targeted to plasma membrane protrusions. J. Biol. Chem., 275: 5512-5520. (* joint first authors).
Maw, M.A., Corbeil, D., Koch, J., Hellwig, A., Wilson-Wheeler, J.C., Bridges, R.J., Kumaramanickavel, G., John, S., Nancarrow, D., Röper, K., Weigmann, A., Huttner, W.B., and Denton, M.J. (2000) A frameshift mutation in prominin (mouse)-like 1 causes human retinal degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 9:27-34.
Corbeil, D.*, Röper, K.*, Hannah, M.J., Hellwig, A., and Huttner, W.B. (1999) Selective Localization of the Polytopic Membrane Protein Prominin in Microvilli of Epithelial Cells- A Combination of Apical Sorting and Retention in Plasma Membrane Protrusions. J. Cell Sci. 112:1023-1033. (* joint first authors).
Corbeil, D., Röper, K., Weigmann, A., and Huttner, W.B. (1998) AC133 hematopoietic stem cell antigen: human homologue of mouse kidney prominin or distinct member of a novel protein family? Blood 91, 2625-2626.