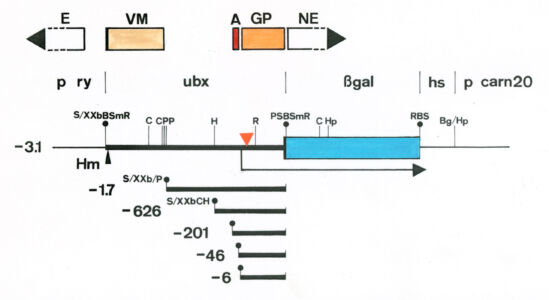
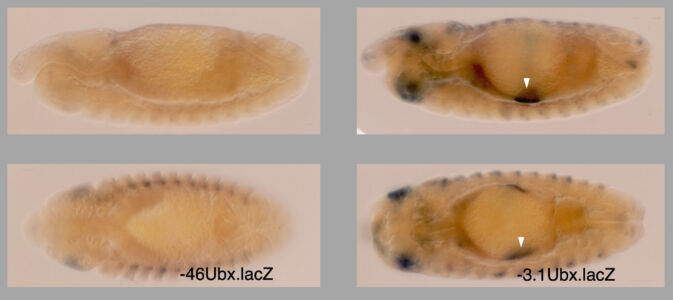
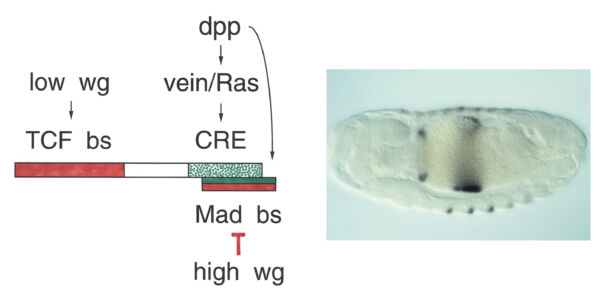
Having defined the cis-regulatory elements within HOX enhancers that respond to extracellular signals, we had the tools to identify the cis-acting factors that bound to these elements to respond to incoming signals. For Dpp, these factors were known to be the sequence-specific DNA-binding SMAD proteins, which turned out to bind to the Dpp-response element within the Ultrabithorax midgut enhancer. CREB and Fos also bind to this enhancer to respond to Vein signalling, but the DNA-binding factor responding to Wingless was unknown.
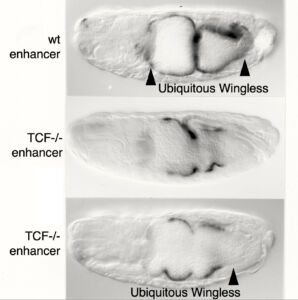
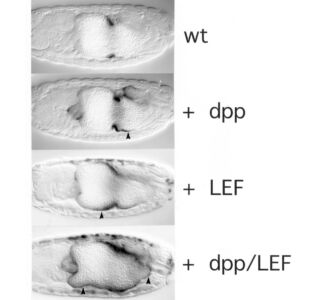
We surmised that this factor would bind directly to Armadillo (Drosophila beta-catenin), known to be the most downstream effector of the Wingless signalling cascade. We therefore used a yeast two-hybrid screen with activated Armadillo as bait to identify this transcription factor, but found a relative of the APC tumour suppressor instead (see below). However, we noticed that the Wnt-responsive elements in the Ultrabithoraxand labial enhancers contained multiple matches to the consensus binding site of TCF/LEF factors. These factors were discovered in mammalian T cells as sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins acting through an enhancer upstream of the T cell receptor-alpha gene. Unusually, these factors cannot activate transcription on their own but depend on cooperation with other transcription factors bound to the same enhancer, including CREB. We thus discovered that Drosophila TCF synergises with SMAD and CREB at the Ultrabithorax midgut enhancer to drive Ultrabithorax expression in the visceral mesoderm. The same three factors also co-operate with Dfos at the labial midgut enhancer to drive Labial expression in the midgut epithelium. Our work corroborated the principle of the context-dependence of TCF/LEF factors discovered by Waterman & Jones in 2001 through their studies of human LEF1.
Relevant references:
- Thali, M., Müller, M.M., DeLorenzi, M., Matthias, P., Bienz, M. (1988)
Drosophila homoeotic genes encode transcriptional activators similar to mammalian OTF-2.
Nature 336(6199): 598-601 - Bienz, M., Saari, G., Tremml, G., Müller, J., Züst, B., Lawrence, P.A. (1988)
Differential regulation of Ultrabithorax in two germ layers of Drosophila.
Cell 53(4): 567-76 - Müller, J., Thüringer, F., Biggin, M., Züst, B., Bienz, M. (1989)
Coordinate action of a proximal homeoprotein binding site and a distal sequence confers the Ultrabithorax expression pattern in the visceral mesoderm.
EMBO J 8(13): 4143-51 - Tremml, G., Bienz, M. (1992)
Induction of labial expression in the Drosophila endoderm: response elements for dpp signalling and for autoregulation.
Development 116(2): 447-56 - Thüringer, F., Cohen, S.M., Bienz, M. (1993)
Dissection of an indirect autoregulatory response of a homeotic Drosophila gene.
EMBO J 12(6): 2419-30 - Bienz, M. (1997)
Endoderm induction in Drosophila: the nuclear targets of the inducing signals.
Curr Opin Genet Dev 7(5): 683-8 - Szüts, D., Freeman, M., Bienz, M. (1997)
Antagonism between EGFR and Wingless signalling in the larval cuticle of Drosophila.
Development 124(16): 3209-19 - Eresh, S., Riese, J., Jackson, D.B., Bohmann, D., Bienz, M. (1997)
A CREB-binding site as a target for decapentaplegic signalling during Drosophila endoderm induction.
EMBO J 16(8): 2014-22 - Riese, J., Yu, X., Munnerlyn, A., Eresh, S., Hsu, S.C., Grosschedl, R., Bienz, M. (1997)
LEF-1, a nuclear factor coordinating signaling inputs from wingless and decapentaplegic.
Cell 88(6): 777-87 - Waltzer, L., Bienz, M. (1998)
Drosophila CBP represses the transcription factor TCF to antagonize Wingless signalling.
Nature 395(6701): 521-5 - Bienz, M. (1998)
TCF: transcriptional activator or repressor?
Curr Opin Cell Biol 10(3): 366-72 - Waltzer, L., Bienz, M. (1999)
The control of beta-catenin and TCF during embryonic development and cancer.
Cancer Metastasis Rev 18(2): 231-46 - Szüts, D., Bienz, M. (2000)
LexA chimeras reveal the function of Drosophila Fos as a context-dependent transcriptional activator.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97(10): 5351-6 - Barker, N., Hurlstone, A., Musisi, H., Miles, A., Bienz, M., Clevers, H. (2001)
The chromatin remodelling factor Brg-1 interacts with beta-catenin to promote target gene activation.
EMBO J 20(17): 4935-43 - Saller, E., Bienz, M. (2001)
Direct competition between Brinker and Drosophila Mad in Dpp target gene transcription.
EMBO Rep 2(4): 298-305 - Waltzer, L., Vandel, L., Bienz, M. (2001)
Teashirt is required for transcriptional repression mediated by high Wingless levels.
EMBO J 20(1-2): 137-45 - Saller, E., Kelley, A., Bienz, M. (2002)
The transcriptional repressor Brinker antagonizes Wingless signaling.
Genes Dev 16(14): 1828-38 - Bienz, M., Clevers, H. (2003)
Armadillo/beta-catenin signals in the nucleus--proof beyond a reasonable doubt?
Nat Cell Biol 5(3): 179-82