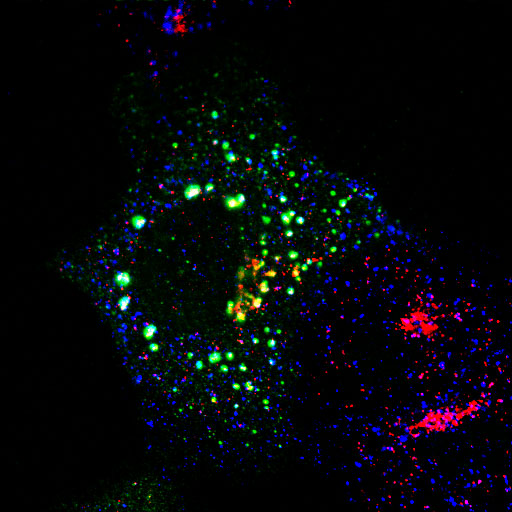
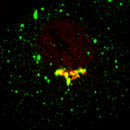
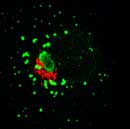
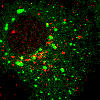
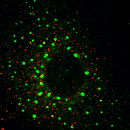
EpsinR L10E overexpression in COS cells
Insertion of a glutamic acid (E) in place of the hydrophobic leucine (L)
is predicted to affect epsinR's ability to bend membranes
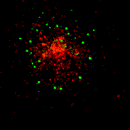
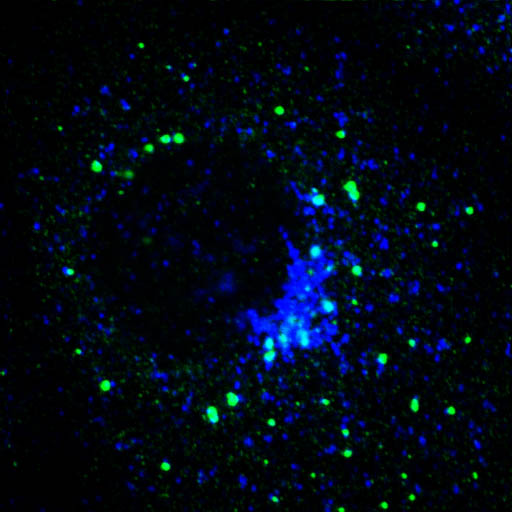
Colocalisation of EpsinR L10E (green) with markers (red), focusing on the perinuclear region.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
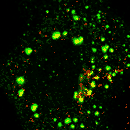
| AP1
Large Image (62 kb) Full field |
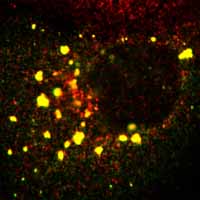
Clathrin |
M6P receptor |
GM130 |
|
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
TGN46 |
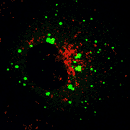
LAMP1 - Red |
EEA1 |
CD63 |
Blue - Transferrin |
Comparison of epsin1 and epsinR
Myc-epsinR (WT) overexpression and colocalisation with markers
Myc-epsinR D34G+R67L (lipid binding mutant)
Myc-epsinR L10E (proposed lipid conformation mutant)
Myc-epsinR D342R+D422R (clathrin binding mutant)
Myc-epsinR D34G+R67L + D342R+D422R (lipid and clathrin binding mutant)