LMB scientists break resolution records to visualise individual atoms with single-particle cryo-EM
Cryo-EM map of mouse apoferritin (blue). Positive density peaks in the difference map (yellow) allows visualization of hydrogen atoms. Credit: Abhay Kotecha.
Looking at the precise three-dimensional arrangement of atoms within a protein helps us to understand how it can perform its functions. Although electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) has developed rapidly as an important structural biology technique in recent years, X-ray crystallography had been the only technique able to visualise individual atoms. Radu Aricescu’s and Sjors Scheres’ groups, in collaboration with scientists at Thermo Fisher Scientific and elsewhere, have now been able to resolve individual protein atoms for the first time in a three-dimensional cryo-EM image.
This collaboration started in early 2019 when Radu and Abhay Kotecha, a researcher at Thermo Fisher Scientific, wanted to test new cryo-EM hardware on a small membrane protein sample. GABAA receptors, a focus of Radu’s research for over a decade, were chosen because the highest achievable resolution using the best available technology seemed to have reached a limit at around 2.5 Ångströms (Å), but higher resolution was clearly needed for better drug design.
What is atomic resolution?
Resolution is usually reported in Ångströms, a unit of length that is one ten-billionth of a metre or 0.1 nanometres, and refers to the smallest distance between which two objects can be seen to be separate.
The length of a typical carbon-carbon bond is 1.5 Å; other bonds in proteins are a bit shorter. Thus, as the resolution gets down to 1.2 Å, it becomes possible to see individual atoms within a protein, achieving true atomic resolution.
While testing new hardware developments that included a cold field emission gun electron source, a new energy filter, and a new camera, the team also had to develop new processing strategies. Algorithms for the correction of optical aberrations that were previously developed by Jasenko Zivanov in Sjors’ group, as well as an algorithm proposed by Chris Russo and Richard Henderson, played crucial roles in squeezing the most information out of the images.
After receiving images collected on the new microscope hardware by Abhay Kotecha at Thermo Fisher Scientific in Eindhoven, Netherlands, Takanori Nakane, a postdoc in Sjors’ group, developed an optimal workflow in RELION and Andrija Sente, along with other members of Radu’s group, used this workflow to process GABAA receptor images, while feeding back results to rapidly optimise microscope settings. A new, high-capacity data storage system developed by Jake Grimmett and Toby Darling in the LMB’s Scientific Computing team offered crucial support to handle the approximately one hundred terabytes of data generated. This sustained team effort led to an unprecedented 1.7 Å resolution GABAA receptor structure.
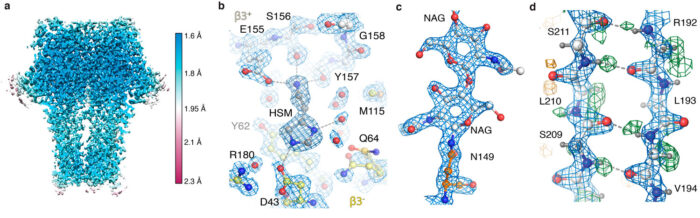
This was the best reported resolution achieved using cryo-EM for any protein sample other than for the protein apoferritin. Apoferritin is commonly used as a benchmark for cryo-EM, because its molecular stability and 24-fold symmetry allow high-resolution reconstructions from relatively few particles.
Using the new hardware and processing strategies, the team were able to obtain a 1.22 Å resolution apoferritin structure, beating the previous 1.53 Å record to be the highest resolution single-particle cryo-EM structure yet obtained. Most impressively, this resolution enabled visualisation of individual hydrogen atoms, even on water molecules inside the protein structure. The visualisation of hydrogen bonding networks inside protein structures and in drug binding pockets allows researchers to better understand how they work.
This work represents the breaking of a key barrier for cryo-EM as a structural biology technique and the new technology, data collection, and processing strategies will expand the number of proteins whose structures can be solved to high resolution. These higher-resolution reconstructions will allow a better understanding of how proteins work and facilitate design of more specific drugs that could impact on treatments for a huge range of diseases.
The work was funded by UKRI MRC, Wellcome, University of Cambridge, Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, Cambridge Trust, European Commission Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions, EMBO, Cancer Research UK, and Boehringer Ingelheim Fonds.
Further references
Single-particle cryo-EM at atomic resolution. Nakane, T., Kotecha, A., Sente, A., McMullan, G., Masiulis, S., Brown, PMGE., Grigoras, IT., Malinauskaite, L., Malinauskas, T., Miehling, J., Uchański, T., Yu, L., Karia, D., Pechnikova, EV., de Jong, E., Keizer, J., Bischoff, M., McCormack, J., Tiemeijer, P., Hardwick, SW., Chirgadza, DY., Murshudov, G., Aricescu, AR., Scheres, SHW. Nature doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2829-0
Sjors’ group page
Radu’s group page
Nature News and Views: Cryo-electron microscopy reaches atomic resolution
Nature News article: ‘It opens up a whole new universe’: Revolutionary microscopy technique sees individual atoms for first time
Previous Insight on Research
Structures of the human GABAA receptor reveal how it functions and could help improve key drugs