YopJ Activation by
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The identification of a cofactor for YopJ |
|
In the previous page we showed how YopJ, a toxin secreted by Yersinia, is an enzyme that inactivates eukaryotic proteins necessary for the innate immune response, thereby suppressing the first line of defense against infection. Serine and threonine residues modified in the active sites of important enzymes are shown. |
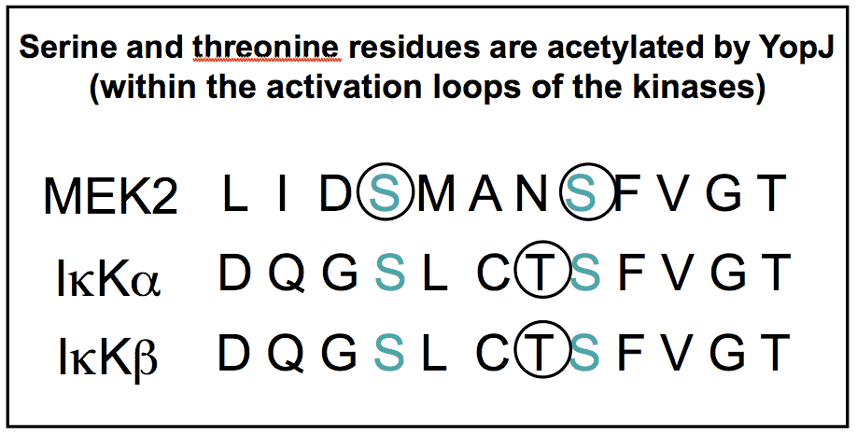 |
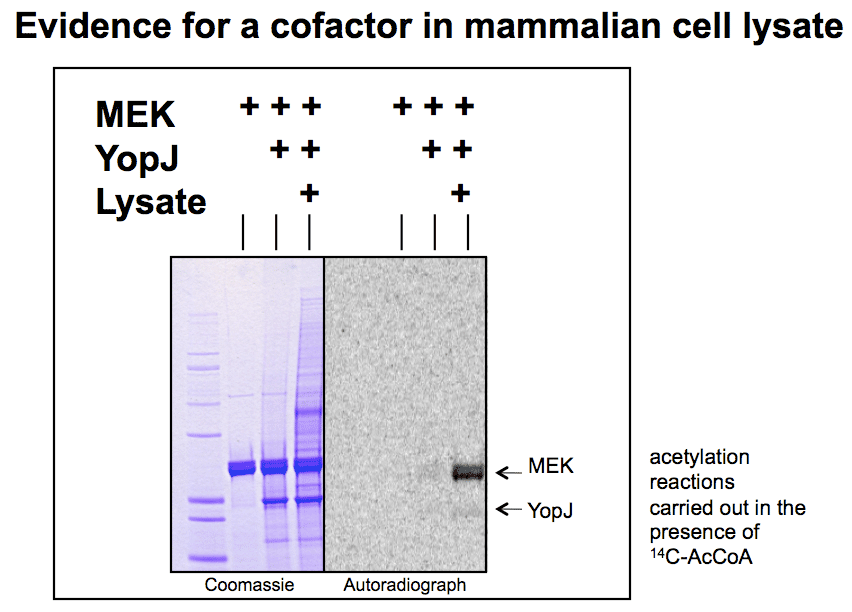
In vitro acetylation reactions using purified YopJ and MEK are inefficient, yet in vivo there is a near complete inactivation of MEK (with levels of YopJ expression that are barely detectable), implying that in cells the enzyme is much more efficient. This prompted us to search for a possible cofactor for YopJ in mammalian cells. |
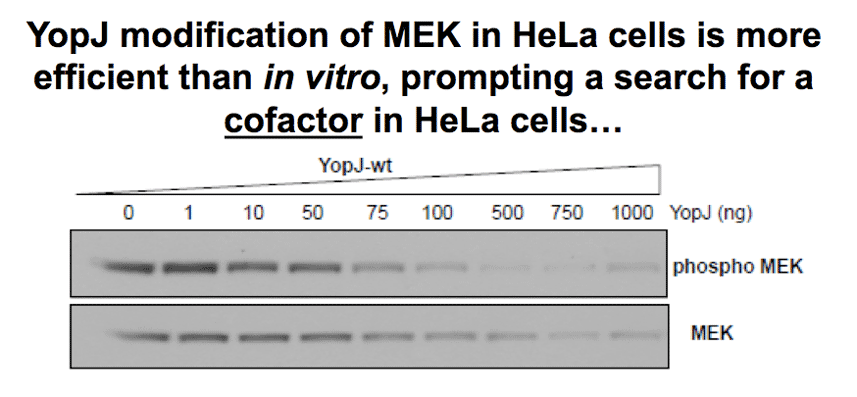 |
Mammalian cell lysate (a few microlitres) gave a robust activation of YopJ acetyltransferase activity. Gel filtration showed the cofactor has a low molecular weight. Surprisingly, the cofactor activity was not lost, even after 18h dialysis (10kDa MWCO) |
 |
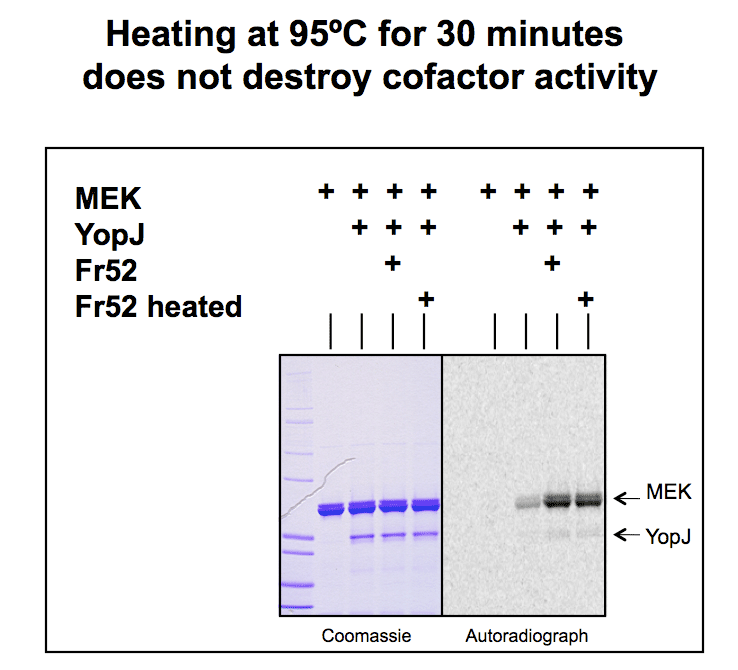
Fraction 52 from the gel filtration (which contained the cofactor) was heated for 30min and it still works, showing the cofactor is heat-stable. |
 |
The YopJ cofactor is a: |
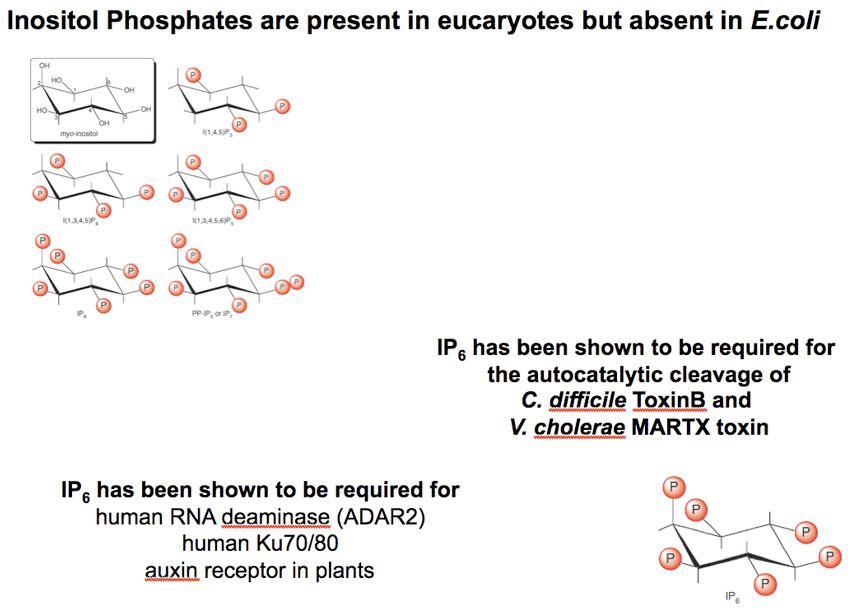 |
IP6 at low nanomolar concentrations stimulates YopJ activity. This result indicates that YopJ is selective in its requirement for phosphate groups and that three phosphates, as in IP3, are insufficient to stimulate the activity of YopJ. |
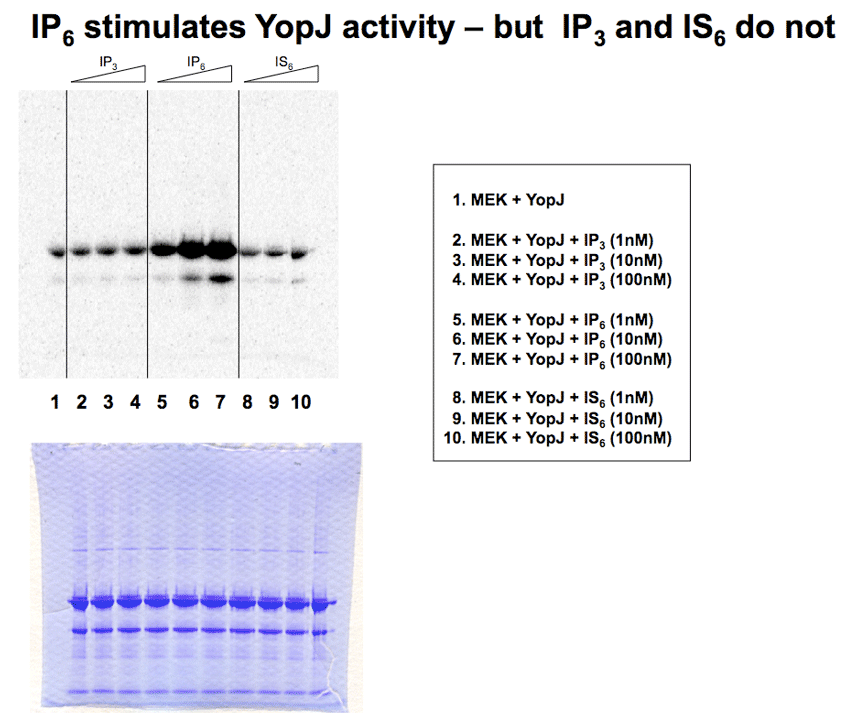 |
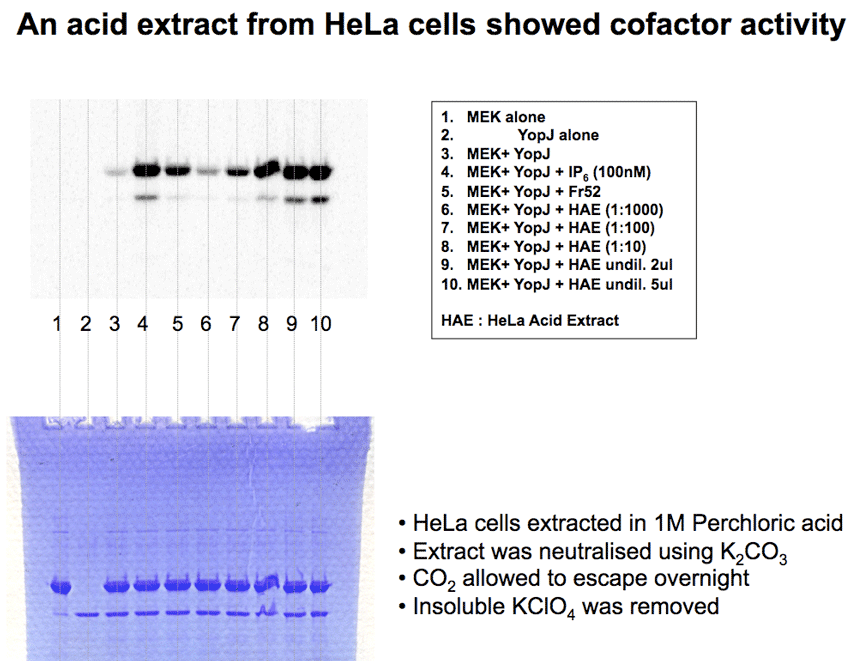 |
|
The cofactor from HeLa cells was purified by anion exchange chromatography and subjected to mass spectrometry... |
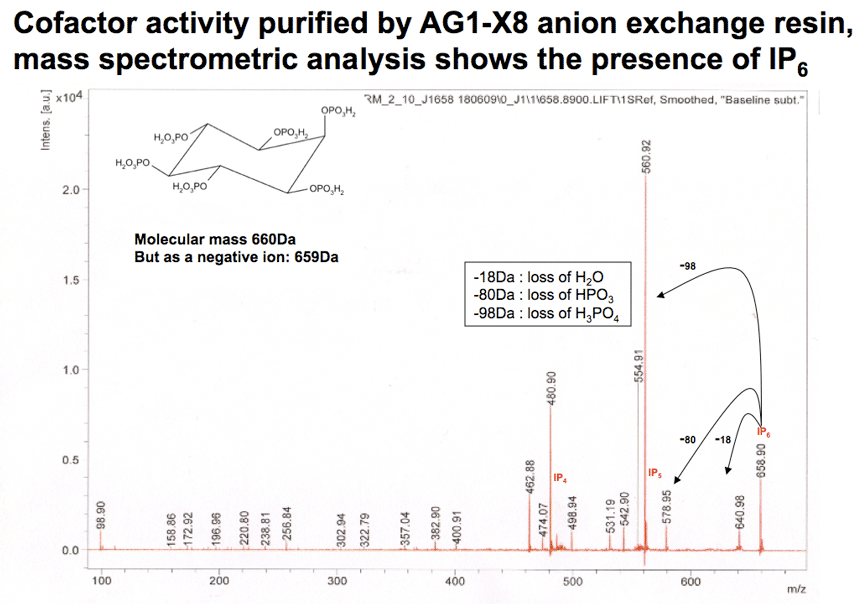 |
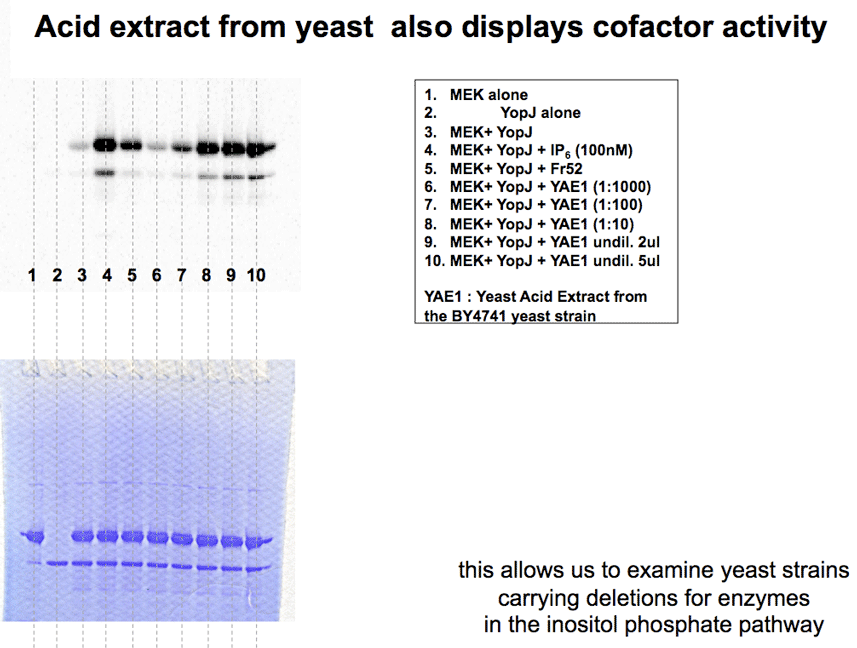
The presence of the cofactor in yeast allowed us to test different deletion yeast strains. Acid extract from the impk(delta) strain of S.cerevisiae was deficient for the YopJ stimulatory cofactor. This strain accumulates IP2 and IP3, but has no IP4, IP5 or IP6. |
 |
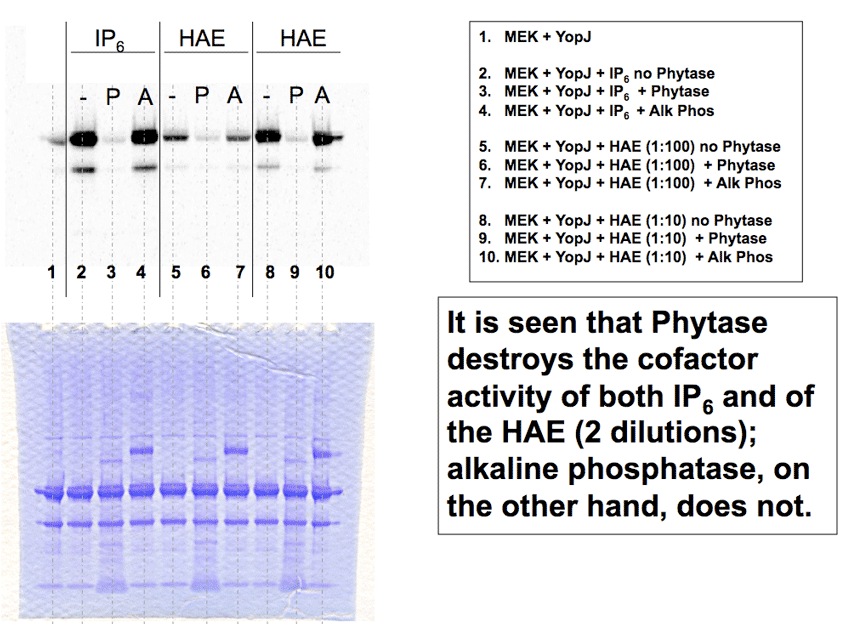
Phytase degrades inositol phosphates and kills the cofactor activity, while a protein phosphatase has no effect. |
 |
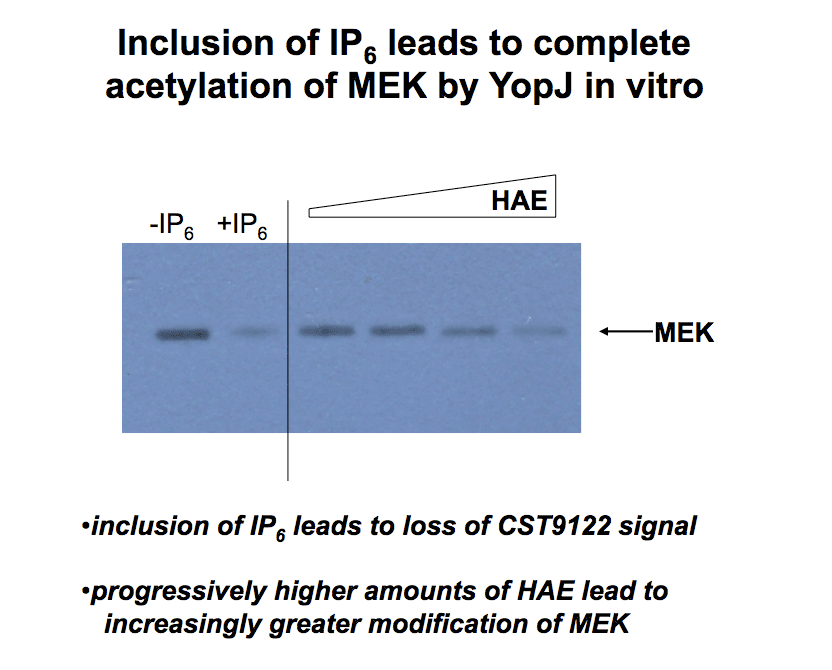
HeLa Acid Extract (HAE) works like IP6 to activate YopJ acetyltransferase activity in vitro, leading to complete modification of MEK. MEK was detected using a discriminatory antibody (CST9122) directed against the activation loop of MEK. When the loop is acetylated then the antibody no longer recognizes MEK. |
 |
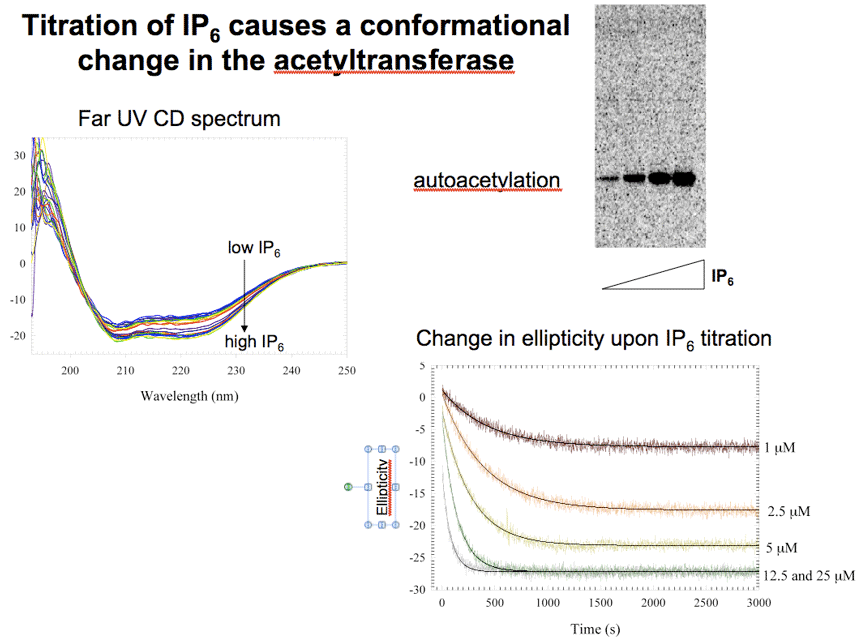
IP6 binding to AvrA (the Salmonella equivalent of YopJ) leads to a change in tertiary structure. By tryptophan fluorescence YopJ also changes conformation on binding to IP6 (not shown). |
 |
Our publications on YopJ
Mittal et al PNAS 2006
Mittal et al JBC 2010
Back to Black Plague and inhibition of innate immunity
Back to The Plague
Back to Research Topics