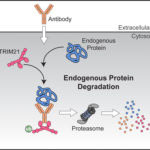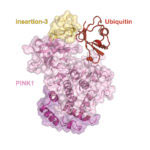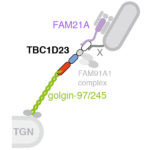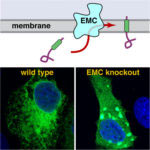
The human genome encodes approximately 5000 membrane-embedded proteins that carry out many essential processes such as cell-to-cell communication, cell adhesion and intracellular trafficking. Almost all of these proteins are assembled at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) by molecular machines that guide them into the membrane. Because these thousands of membrane proteins are highly diverse in size, shape and charge, different machines are needed for different types of membrane proteins.