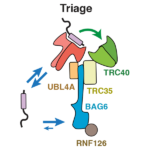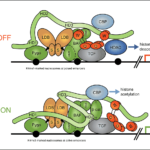
The Wnt signalling pathway is an ancient cell communication pathway that has important roles in development and cancer. Wnt signals elicit context-dependent transcriptional responses by stabilising a cytoplasmic effector called beta-catenin. This controls the embryonic development of tissues and organs in all animals, from the most primitive ones all the way to humans.