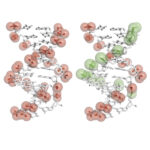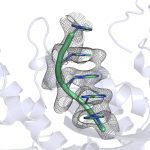
Our genetic code is translated from DNA into proteins through an intermediate molecule: messenger RNA (mRNA). One major way in which synthesis of proteins can be regulated is through turnover of mRNA; less protein is produced from a short-lived mRNA molecule. The signal for the degradation of a particular mRNA is the removal of a stretch of adenosines (As) at the end of the molecule, known as the poly(A) tail.