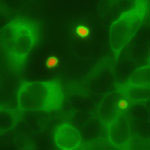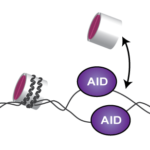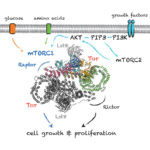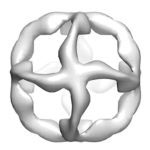
Circadian clocks are found across all higher species, controlling daily rhythms of behaviour and physiology. They are thought to “tick” by producing and then degrading circadian proteins on a 24 hour cycle. At a molecular level, they typically involve expression of “clock” genes that are inhibited approximately every 24 hours by the proteins they encode.