

The contents of eukaryotic cells are organised and moved around by motor proteins running along the tracks that make up the cytoskeleton (microtubules and actin filaments). The largest and most complicated of these motors is cytoplasmic dynein. It is involved with numerous processes, from positioning organelles, to cell division, to clearing up misfolded proteins. Defects in dynein are linked to developmental disorders and neurodegeneration. Dynein is also used by viruses, such as herpes and rabies, to infect the cell. Our goal is to understand how dynein contributes to medically-relevant, cell-biological processes.
We used X-ray crystallography to solve structures of dynein’s motor, which explained how it uses ATP to move along microtubules. We have since taken advantage of advances in cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) to determine how dynein, and its cofactor dynactin, bind the adaptors that link them to cargos. We showed how formation of dynein/dynactin/adaptor complexes activates long distance transport and how this process is controlled by the dynein regulator LIS1.
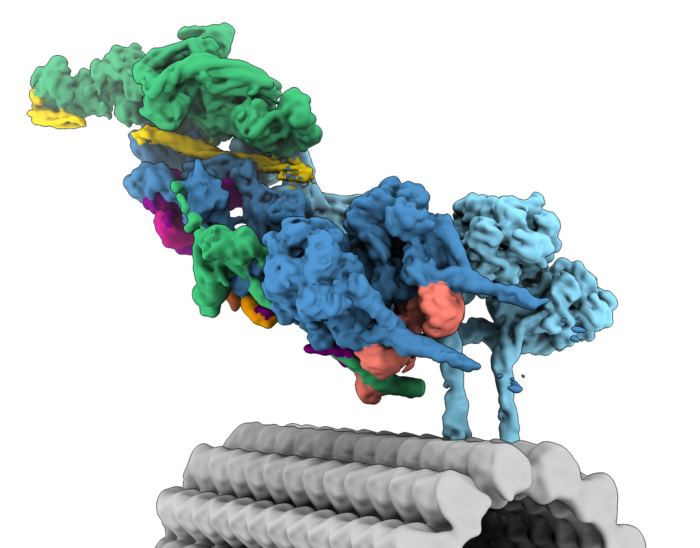
We are interested in the many structural and mechanistic questions that surround dynein transport. How can one dynein complex carry so many different cargos? What mechanisms control whether dynein or the opposite direction kinesin motors are engaged? How do viruses and other pathogens hijack motors? To answer these, we will combine biophysical and cell biological methods with the latest techniques in structural biology.
Selected Papers
- Singh K, Lau CK, Manigrasso G, Gama JB, Gassmann R, Carter AP (2023)
Molecular mechanism of dynein-dynactin activation by JIP3 and LIS1.
Science 383: eadk8544 - Fellows AD, Bruntraeger M, Burgold T, Bassett AR, Carter AP (2023)
Dynein and dynactin move long-range but are delivered separately to the axon tip
J Cell Biol. 223: e202309084 - Chaaban S and Carter AP (2022)
Structure of dynein-dynactin on microtubules shows tandem recruitment of cargo adaptors
Nature 610: 212-216 - Mali GR, Ali FA, Lau CK, Begum F, Boulanger J, Howe JD, Chen ZA, Rappsilber J, Skehel M, Carter AP (2021)
Shulin packages axonemal outer dynein arms for ciliary targeting
Science 371(6532): 910-916. - Zhang K, Foster HE, Rondelet A, Lacey SE, Bahi-Buisson N, Bird AW, Carter AP. (2017)
Cryo-EM Reveals How Human Cytoplasmic Dynein Is Auto-inhibited and Activated.
Cell 169(7): 1303-1314 - Urnavicius, L., Zhang, K., Diamant, A.G., Motz, C., Schlager, M.A., Yu, M., Patel, N.A., Robinson, C.V. and Carter, A.P (2015)
The structure of the dynactin complex and its interaction with dynein.
Science 347: 1441-1446 - Schmidt, H., Zalyte, R., Urnavicius, L. and Carter, A.P (2015)
Structure of human cytoplasmic dynein-2 primed for its power stroke.
Nature 518: 435-438 - Schlager, M.A., Hoang, H.T., Urnavicius, L., Bullock, S.L. and Carter, A.P. (2014)
In vitro reconstitution of a highly processive recombinant human dynein complex.
EMBO J 33: 1855-1868
Group Members
- Sami Chaaban
- Verena Cmentowski
- Ennio d'Amico
- Guoling Fu
- Leon Michalski
- Kashish Singh
- Chisato Tsuji
- Noor Verwei
- Richard Wademan