

William Schafer
Cellular and molecular mechanisms of behaviour
wschafer@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.ukPersonal group site
Elucidating the mechanisms by which nervous systems process information and generate behaviour is among the fundamental problems of biology. Ultimately, it is desirable to understand these processes at the most basic level, that of molecules and cells.
We are investigating these questions using the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, which has an anatomically simple and well-defined nervous system and is tractable to molecular and classical genetic analysis.
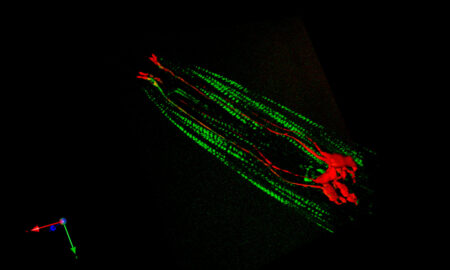
Using a range of approaches, including optogenetic neuroimaging, high content behavioural phenotyping, and electrophysiological analysis of heterologously-expressed receptors and channels, we hope to uncover fundamental principles of nervous system function at the molecular and circuit levels.
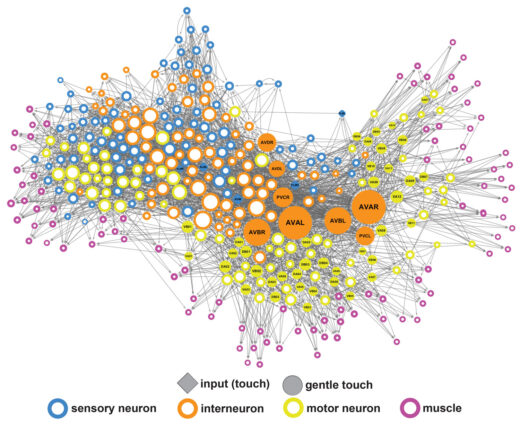
At the molecular level, we are particularly interested in identifying the molecules responsible for ionotropic sensory transduction, which underlies the senses of touch, hearing, sour and salt taste, and pain, and discovering how they couple sensory stimuli to the control of neuronal activity. At the circuit level, we have focused on understanding how monoamine and peptide neuromodulators, often acting extrasynaptically, control brain states and mediate neural plasticity and learning. We are also applying network science approaches to probe the structures of synaptic and extrasnaptic connectomes, with the aim of understanding conserved computational principles implemented in larger and more complex brains.
Selected Papers
- Ripoll-Sánchez, L., Watteyne, J., Sun, H., Fernandez, R., Taylor, S.R., Weinreb, A., Bentley, B.L., Hammarlund, M., 3rd, D.M.M., Hobert, O., Beets, I., Vértes, P.E., Schafer, W.R. (2023)
The neuropeptidergic connectome of C. elegans
Neuron 111(22): 3570-3589 - Morud J, Hardege I, Liu H, Wu T, Choi MK, Basu S, Zhang Y, Schafer WR (2021)
Deorphanisation of novel biogenic amine-gated ion channels identifies a new serotonin receptor for learning.
Curr Biol 31: 4282-4292. - Tang YQ, Lee SA, Rahman M, Vanapalli SA, Lu H, Schafer WR (2020)
Ankyrin is an intracellular tether for TMC mechanotransduction channels.
Neuron 107: 112-125. - Chew YL, Tanizawa Y, Cho Y, Zhao B, Yu AJ Ardiel EL, Rabinowitch I, Bai J, Rankin CH, Lu H, Beets I, Schafer WR (2018)
An afferent neuropeptide system transmits mechanosensory signals triggering sensitization and arousal in C. elegans.
Neuron 99: 1233–1246. - Yan, G., Vértes, P.E., Towlson, E.K., Chew, Y.L., Walker, D.S., Schafer, W.R. and Barabási, A-L. (2017)
Network control principles predict neuron function in the Caenorhabditis elegans connectome.
Nature10.1038/nature24056. - Bentley, B., Branicky, R.S., Barnes, C.L., Chew, Y.L., Yemini, E., Bullmore, E.T., Vértes, P.E. and Schafer, W.R. (2016)
The multilayer connectome of Caenorhabditis elegans
Plos Comput Biol 12(12): e1005283. - Yemini E, Jucikas T, Grundy LJ, Brown AEX, Schafer WR (2013)
A database of C. elegans behavioral phenotypes.
Nat Meth 10: 977-879. - Chatzigeorgiou, M., Bang, S., Hwang, S.W. and Schafer, W.R. (2013)
tmc-1 encodes a sodium-sensitive channel required for salt chemosensation in C. elegans.
Nature 494: 95-99. - Suzuki, H., Thiele, T., Faumont, S., Ezcurra, M., Lockery, S. and Schafer, W.R. (2008)
Functional asymmetry in C. elegans salt taste neurons and its computational role in chemotaxis behaviour
Nature 454: 114-117.
Group Members
- Isabel Beets
- Isabel Conze
- Amy Courtney
- Joseph Gehler
- Jun Meng
- Lidia Ripoll Sanchez
- Keertana Venkatesh
- Denise Walker
- Xinyi Yang