

The Zlatic lab aims to understand the relationship between the structure of the nervous system and its function and to discover the basic principles by which neural circuits implement fundamental computations. A major focus of our research is the circuit implementation of learning and decision-making. For the nervous system to select appropriate responses to multiple, often conflicting cues present in the environment it must be able to 1) learn which sensory cues are associated with rewards and punishments; 2) compute the “predicted value” of each action based on the learnt information; 3) select one action and suppress other physically incompatible competing actions; 4) update memories when predicted and actual outcomes differ to improve future decision-making.
We aim to discover the circuit motifs that implement these four functions, the comprehensive set of structural changes in the brain that are involved in storing specific memories, and the genes required in specific neurons for these computations. We use the tractable genetic model system, the Drosophila melanogaster larva which has the same ground-plan as the adult Drosophila and other insects, but contains fewer (ca. 12,000) and smaller neurons. In this system we can i) image the entire nervous system at synaptic resolution with electron microscopy, and map complete circuits with synaptic resolution, ii) record individual neurons with patch-clamp, iii) image the activity of all neurons at once in intact animals (through the transparent cuticle) with light-sheet microscopy, iv) constrain models of circuit function with comprehensive structural and functional connectivity maps, and iv) use powerful genetic tools to selectively manipulate individual neurons to test models’ predictions and elucidate the functional roles of specific circuit motifs.
EM Reconstruction of the Learning Center (Mushroom Body)
Automated high-throughput behavior detection

Selected Papers
- Winding, M; Pedigo, B.D.; Barnes, C.L.; Patsolic, H.G.; Park, Y; Kazimiers, T; Fushiki, A; Andrade, I.V.; Khandelwal, A; Vales-Aleman, J; Li, F; Randel, N; Barsotti, E; Correia, A; Fetter, R.D.; Hartenstein, V; Preiebe, C.E.; Volgelstein, J.T.; Cardona, A; and Zlatic, M (2023)
The connectome of an insect brain
Science 6636:- Insight on Research : Complete synaptic-resolution connectome of an insect larval brain
- Nature : Gigantic map of fly brain is a first for a complex animal
- Spectrum : Wiring map reveals how larval fruit fly brain converts sensory signals to movement
- Science News : Scientists have mapped an insect brain in greater detail than ever before
- Sky News : First map of insect brain signals 'big step forward' in understanding thoughts
- SMC : Reactions: first whole-brain connectome of an insect brain obtained
- Croteau-Chonka EC, Clayton M, Venkatasubramanian L, Harris SN, Jones BMW, Narayan L, Winding M, Masson JB, Zlatic M, Klein KT. (2022)
High-throughput automated methods for classical and operant conditioning of Drosophila larvae
ElifeOct 28;11:e70015. - Corrales M, Cocanougher BT, Kohn AB, Wittenbach JD, Long XS, Lemire A, Cardona A, Singer RH, Moroz LL, Zlatic M. (2022)
A single-cell transcriptomic atlas of complete insect nervous systems across multiple life stages.
Neural DevAug 24;17(1):8. - Eschbach C, Fushiki A, Winding M, Afonso B, Andrade IV, Cocanougher BT, Eichler K, Gepner R, Si G, Valdes-Aleman J, Fetter RD, Gershow M, Jefferis GS, Samuel AD, Truman JW, Cardona A, Zlatic M. (2021)
Circuits for integrating learned and innate valences in the insect brain.
ElifeNov 10;10: e62567. - Cocanougher B. T., Wittenbach J. D., Long X., Kohn A. B., Norekian T. P., Yan J., Colonell J., MassonJ. B., Truman J. W., Cardona A., Turga S., Singer R. H., Moroz L. L., and Zlatic M. (2019)
Comparative single-cell transcriptomics of complete insect nervous systems.
bioRXivdoi: https://doi.org/10.1101/785931 - Valdes-Aleman J., Fetter R. D., Sales E. C., Heckman E. L., Doe C. Q., Landgraf M., Cardona A. and Zlatic M. (2021)
Comparative Connectomics Reveals How Partner Identity, Location, and Activity Specify Synaptic Connectivity in Drosophila.
NeuronJan 6;109(1):105-122.e7. - Eschbach C., Fushiki A., Winding M., Schneider-Mizell C. M., Shao M., Arruda B., Eichler K., Valdes-Aleman J., Thum A. S., Gerber B., Fetter R. D., Truman W. J., Litwin-Kumar A., Cardona A. and Zlatic M. (2020)
Recurrent architecture for adaptive regulation of learn in the insect brain.
Nature NeuroscienceApr;23(4):544-555. - Masson J. B., Laurent F., Cardona A., Barre C., Skatchkovsky N., Zlatic M. and Jovanic T. (2020)
Identifying neural substrates of competitive interactions and sequence transitions during mechanosensory responses in Drosophila.
PLoS GeneticsFeb 14;16(2):e1008589. - Jovanic T., Winding M., Cardona A., Truman J. W., Gershow M. and Zlatic M. (2019)
Neuronal substrates of Drosophila larval anemotaxis.
Current Biology29(4):554-566.e4. - Eichler K., Li F., Kumar A. L., Andrade I., Schneider-Mizell C., Saumweber T., Huser A., Gerber, B., Fetter R. D., Truman J. W., Abbott L. F., Thum A., Zlatic, M. and Cardona A. (2017)
The complete connectome of a learning and memory centre in an insect brain.
NatureAug 9;548(7666):175-182. - Jovanic, T. S.-M., C.M.; Shao, M.; Masson, J.B.; Denisov, G.; Fetter, R.D.; Truman, J.W.; Cardona, A. and Zlatic, M. (2016)
Competitive disinhibition in early sensory processing mediates behavioral choice and sequences in Drosophila.
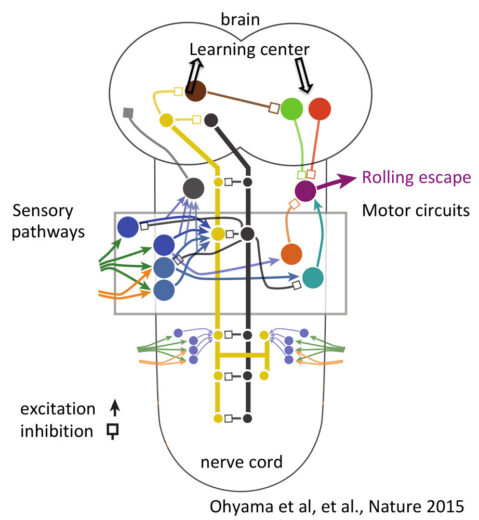
CellOct 20;167(3):858-870.e19. - Ohyama, T. et al. (2015)
A multilevel multimodal circuit enhances action selection in Drosophila.
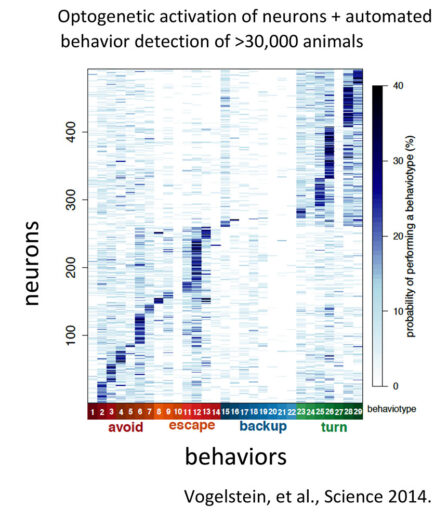
Nature520(7549):633-9. - Vogelstein, J. T. et al. (2014)
Discovery of brainwide neural-behavioral maps via multiscale unsupervised structure learning.
Science344(6182):386-92.
...
Group Members
- Bernd Breuer
- Nicolo Ceffa
- Michael Clayton
- Amina Dulac
- Basel El Galfi
- Samuel Harris
- Ivana Henry
- Nan Hu
- François Laurent
- Chu-Cheng Lin
- George Mo
- Nadine Randel
- Miranda Robbins
- Mohammad Hadi Saiepour
- Andrey Stoychev
- Lalanti Venkatasubramanian
- Kun Wang
- Sicheng Wen