

Tanmay Bharat
Role of Surface Molecules in Microbial Multicellularity
tbharat@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.ukPersonal group site
Our laboratory uses electron cryo-tomography (cryo-ET) to study how surface molecules allow microorganisms (bacteria and archaea) to form multicellular communities. We develop novel correlative imaging and image processing techniques to support our inquiries. Surface molecules play key roles in mediating cell-cell interactions, which underpin the formation of biofilms and microbiomes.
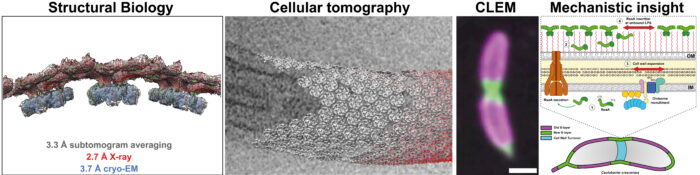
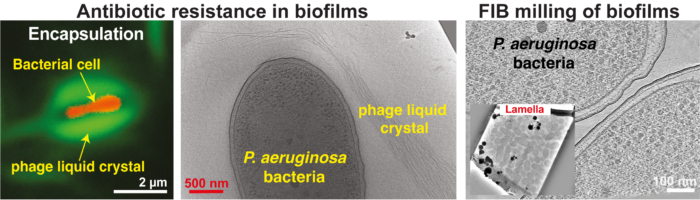
While structural biology of many cell surface molecules reveals fundamental information about bacterial and archaeal cell-cell interactions, our work has clear biomedical relevance. For example, surface molecules allow pathogenic bacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Mycobacterium tuberculosis to evade antibiotics by forming biofilms during infection.
Governing principles of biofilm formation revealed by advanced cryo-ET imaging (right).
With our fundamental work, our goal is to unravel general principles governing multicellular interactions in microbes, to understand how emergent properties such as antibiotic tolerance arise within multicellular communities of prokaryotes. We have utilised the fundamental molecular mechanisms revealed in our work to develop approaches to disrupt pathogenic microbial biofilms, which we are further developing in collaboration with clinicians.
Selected Papers
- Kügelgen, A.v., Cassidy, C.K., Dorst, S.v., Pagani, L.L., Batters, C., Ford, Z., Löwe, J., Alva, V., Stansfeld, P.J., Bharat, T.A.M. (2024)
Membraneless channels sieve cations in ammonia-oxidizing marine archaea
Nature 630: 230-236 - Böhning, J., Graham, M., Letham, S.C., Davis, L.K., Schulze, U., Stansfeld, P.J., Corey, R.A., Pearce, P., Tarafder, A.K., Bharat, T.A.M. (2023)
Biophysical basis of filamentous phage tactoid-mediated antibiotic tolerance in P. aeruginosa
Nat Commun 14 (1): 8429 - Böhning, J., Ghrayeb, M., Pedebos, C., Abbas, D.K., Khalid, S., Chai, L., Bharat, T.A.M. (2022)
Donor-strand exchange drives assembly of the TasA scaffold in Bacillus subtilis biofilms.
Nat Commun 13: 7082 - Melia, C., Bolla, J.R., Lanwermeyer, S.K., Mihaylov, D., Hoffmann, P.C., Huo, J., Wozny, M.R., Elfari, L.M., Böhning, J., Owens, R.J., Robinson, C.V., O’Toole, G.A., Bharat, T.A.M. (2021)
Architecture of cell-cell junctions in situ reveals a mechanism for bacterial biofilm inhibition.
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118(31): e2109940118 - von Kügelgen, A., Tang., H., Hardy, G.G., Kureisaite-Ciziene, D., Brun, Y.V., Stansfeld, P.J., Robinson, C.V., and Bharat, T.A.M. (2020)
In Situ Structure of an Intact Lipopolysaccharide-Bound Bacterial Surface Layer
Cell 180(2): 348-358 - Tarafder, A.K., et al., von Kügelgen, A., Mellul, A., Schulze, U., Aarts, D. and Bharat, T.A.M (2020)
Phage liquid crystalline droplets form occlusive sheaths that encapsulate and protect infectious rod-shaped bacteria
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Group Members
- Jan Böhning
- Ido Caspy
- Camila Clemente
- Zephyr Ford
- Julia Gordeeva
- Buse Isbilir
- Kenny Jungfer
- Eloise Mawdesley
- Hannah Ochner
- Olivia Smith
- Abul Tarafder
- Bogdan Toader
- Andriko von Kügelgen
- Zhexin (Eric) Wang
- Yuexuan Zhang