

Abnormal filamentous inclusions characterize many human neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. The formation of filaments or their mere presence is believed to result in the propagation of inclusions and neurodegeneration. Our work showed that the intracellular filaments of these diseases are made of either tau or alpha-synuclein. Others established that the extracellular deposits of Alzheimer’s disease are made of amyloid-beta.
We and others identified mutations in MAPT, the tau gene, that cause inherited forms of frontotemporal dementia with abundant tau inclusions, establishing a central role for tau assembly. SNCA, the alpha-synuclein gene, is mutated or multiplied in inherited cases of Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies, and we showed that alpha-synuclein is the major component of the filamentous inclusions of Parkinson’s disease, other Lewy body disorders and multiple system atrophy.
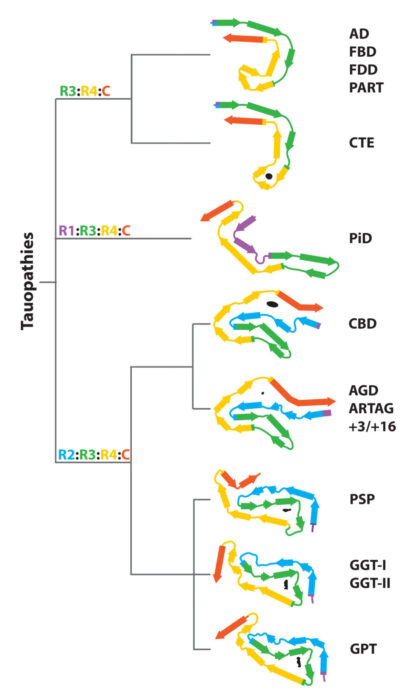
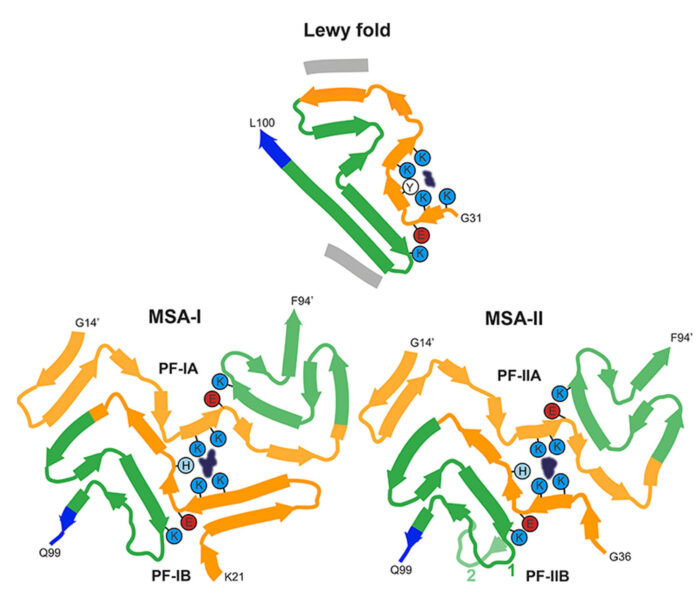
In collaboration with Sjors Scheres, we are using electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) to determine the structures of pathological amyloid filaments made of assembled tau, alpha-synuclein and amyloid-beta 42. We have also shown that cryo-EM can be used to identify previously unknown amyloid filaments and new disease entities. Each tauopathy is characterized by its own filament conformation, but some tauopathies share the same conformation, for example Alzheimer’s disease and primary age-related tauopathy. For synucleinopathies, we have established that disorders with Lewy bodies, such as Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies, share the same fold, which is different from the folds of multiple system atrophy. For tauopathies and synucleinopathies, differences in conformation are between some diseases, not between individuals with a given disease.
To better understand mechanisms of disease, it is important to develop methods for forming amyloid filaments like those from human brains. As a first step, we have shown that recombinant tau (297-391) assembles in vitro into filaments that are identical to the paired helical filaments of Alzheimer’s disease.
Selected Papers
- Yang, Y., Shi, Y., Schweighauser, M., Zhang, X., Kotecha, A., Murzin, A.G., Garringer, H.J., Cullinane, P.W., Saito, Y., Foroud, T., Warner, T.T., Hasegawa, K., Vidal, R., Murayama, S., Revesz, T., Ghetti, B., Hasegawa, M., Lashley, T., Scheres, S.H.W. and Goedert, M. (2022)
Structures of α-synuclein filaments from human brains with Lewy pathology.
Nature 610: 791-795. - Lövestam, S., Koh, F.A., van Knippenberg, B., Kotecha, A., Murzin, A.G., Goedert, M. and Scheres, S.H.W. (2022)
Assembly of recombinant tau into filaments identical to those of Alzheimer’s disease and chronic traumatic encephalopathy.
eLife 11: e76494. - Schweighauser, M., Arseni, D., Bacioglu, M., Huang, M., Lövestam, S., Shi, Y., Yang, Y., Zhang, W., Kotecha, A., Garringer, H.J., Vidal, R., Hallinan, G.I., Newell, K.L., Tarutani, A., Murayama, S., Miyazaki, M., Saito, Y., Yoshida, M., Hasegawa, K., Lashley, T., Revesz, T., Kovacs, G.G., van Swieten, J., Takao, M., Hasegawa, M., Ghetti, B., Spillantini, M.G., Ryskeldi-Falcon, B., Murzin, A.G., Goedert, M. and Scheres, S.H.W. (2022)
Age-dependent formation of TMEM106B amyloid filaments in human brains.
Nature 605: 310-314. - Yang, Y., Arseni, D., Zhang, W., Huang, M., Lövestam, S., Schweighauser, M., Kotecha, A., Murzin, A.G., Peak-Chew, S.Y., Macdonald, J., Lavenir, I., Garringer, H.J., Gelpi, E., Newell, K.L., Kovacs, G.G., Vidal, R., Ghetti, B., Ryskeldi-Falcon, B., Scheres, S.H.W. and Goedert, M. (2022)
Cryo-EM structures of amyloid-β 42 filaments from human brains.
Science 357: 167-172. - Macdonald J.A., Chen, J.L., Masuda-Suzukake, M., Schweighauser, M., Jaunmuktane, Z., Warner, T., Holton, J.L., Grossman, A., Berks, R., Lavenir, I. and Goedert, M. (2021)
Assembly of α-synuclein and neurodegeneration in the central nervous system of heterozygous M83 mice following the peripheral administration of α-synuclein seeds.
Acta Neuropathologica Communications 9: 189. - Shi, Y., Zhang, W., Yang, Y., Murzin, A.G., Falcon, B., Kotecha A, van Beers, M., Tarutani, A., Kametani, F., Garringer, H.J., Vidal, R., Hallinan, G.I., Lashley, T., Saito, Y., Murayama, S., Yoshida, M., Tanaka, H., Kakita, A., Ikeuchi, T., Robinson, A.C., Mann, D.M.A., Kovacs, G.G., Revesz, T., Ghetti, B., Hasegawa, M., Goedert, M. and Scheres, S.H.W. (2021)
Structure-based classification of tauopathies.
Nature 598: 395-363. - Shi, Y., Murzin, A.G., Falcon, B., Epstein, A., Machin, J., Tempest, P., Newell, K.L., Vidal, R., Garringer, H.J., Sahara, N., Higuchi, M., Ghetti, B., Jang, M.-K., Scheres, S.H.W. and Goedert, M. (2021)
Cryo-EM structures of tau filaments from Alzheimer’s disease with PET ligand APN-1607.
Acta Neuropathologica 141: 697-709. - Lövestam, S., Schweighauser, M., Matsubara, T., Murayama, S., Tomita, T., Ando, T., Hasegawa, K., Yoshida, M., Tarutani, A., Hasegawa, M., Goedert, M. and Scheres, S.H.W. (2021)
Seeded assembly in vitro does not replicate the structures of α-synuclein filaments from multiple system atrophy.
FEBS Open Bio 11: 999-1013.
Group Members
- Yeongjin Baek
- Melissa Huang
- Simon Knoblauch
- Sofia Lövestam
- Jennifer Macdonald
- John Walker